Last week I talked about scheduling start/stop of your Amazon EC2 instances to save costs.
You can read the post here.
You can read the post here.
Amazon charges for their instances on per-hour basis
So do you want to save costs be stopping your RDS Instances during the off-hours (nights, weekends etc.)?
This post is going to describe a fairly easy process for this setup using AWS Lambda and CloudWatch
Note: First one million Lambda requests per month are free.
Let's jump to the process now...
So do you want to save costs be stopping your RDS Instances during the off-hours (nights, weekends etc.)?
This post is going to describe a fairly easy process for this setup using AWS Lambda and CloudWatch
Setup
We would be triggering a Lambda function from CloudWatch Scheduler which will in turn start/stop your RDS instances based on the Tags applied.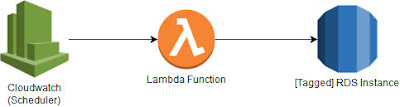 |
| Diag 1: RDS Scheduler Setup |
Note: First one million Lambda requests per month are free.
Let's jump to the process now...
Create an IAM Role for Lambda
In order to manage the RDS Instances using Lambda, we will have to create an IAM Role which we would later attach to the Lambda Function
- Under IAM Roles, select Create Role
- Select Lambda as the trusted entity for this role
- On the permissions page, select Create policy. This would open up a new window
- Select Create Your Own Policy
- Enter a suitable policy name and description
- Enter the following JSON code in the Policy Document
- Now go back to the previous window (Create Role) and attach the policy you created to the role
Note: If the policy is not visible yet, try refreshing the list - Provide a suitable Role name and description on the review screen and create the role.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"rds:StopDBInstance",
"rds:StartDBInstance",
"rds:Describe*",
"rds:ListTagsForResource"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Validate and save the policy
Create the Lambda Function
For this purpose, I would be using Python code inside Lambda using Python Boto3 libraries. Don't worry if you are not familiar with Python. The instruction here should suffice!
- Go to AWS Lambda Console and Create function
- For our purpose, we will Author from scratch
- Provide a suitable name to the Lambda Function and Choose an existing role (the one we have created in the last step)
- Configure the Lambda Function with following details:
Code entry type: Edit code inline
Runtime: Python 2.7
Handler: lambda_function.lambda_handler - In the code block, clear out everything and add the code from the following URLs
Stop RDS Instances
Start RDS Instances
NOTE: - Python is indentation sensitive. Please be careful with the copy-paste
- The script will action on the RDS instances with a specific tag (will setup this in next section)
- In the Basic settings, increase the timeout from 3 sec to 10 sec.
- Save the function.
| Diag 2: Lambda Function Definition |
Repeat Steps 1-7 for creating another function to Schedule Start of RDS Instances.
Setting up CloudWatch Trigger
In the Lambda Function, select Triggers tab and Add a new trigger
Select CloudWatch Events as the Source
TAG1
Select CloudWatch Events as the Source
- Create a new rule
- Specify appropriate Rule name and description
- You can enter schedule expression as per your need to invoke the trigger
For Example:
cron(00 23 ? * MON-FRI *)
// This will invoke the Lambda function every Monday-Friday at 23:00 PM GMT
Tagging RDS Instance
The last and most simplest part of this setup is to tell Lambda which RDS Instances to stop/start.
This can simply be done by defining the following Tag in your RDS Instances
TAG1
Name: AutoRestart
And that's it!!
Cheers!
No comments:
Post a Comment